Goat Anti-HPK1 / MAP4K1 Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92918 |
| Other Accession | NP_009112, 11184 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat, Pig, Dog |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 91296 Da |
| Gene ID | 11184 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1, 2.7.11.1, Hematopoietic progenitor kinase, MAPK/ERK kinase kinase kinase 1, MEK kinase kinase 1, MEKKK 1, MAP4K1, HPK1 |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~N/A |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-HPK1 / MAP4K1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MAP4K1 (HGNC:6863) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HPK1 |
| Function | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, which plays a role in the response to environmental stress (PubMed:24362026). Appears to act upstream of the JUN N-terminal pathway (PubMed:8824585). Activator of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. MAP4Ks act in parallel to and are partially redundant with STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST2 in the phosphorylation and activation of LATS1/2, and establish MAP4Ks as components of the expanded Hippo pathway (PubMed:26437443). May play a role in hematopoietic lineage decisions and growth regulation (PubMed:24362026, PubMed:8824585). Together with CLNK, it enhances CD3-triggered activation of T-cells and subsequent IL2 production (By similarity). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed primarily in hematopoietic organs, including bone marrow, spleen and thymus. Also expressed at very low levels in lung, kidney, mammary glands and small intestine |
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
References
Phosphorylation of CARMA1 by HPK1 is critical for NF-kappaB activation in T cells. Brenner D, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009 Aug 25. PMID 19706536.
Proteasome-mediated degradation and functions of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 in pancreatic cancer. Wang H, et al. Cancer Res, 2009 Feb 1. PMID 19141650.
Prostaglandin E2 activates HPK1 kinase activity via a PKA-dependent pathway. Sawasdikosol S, et al. J Biol Chem, 2007 Nov 30. PMID 17895239.
Caspase-cleaved HPK1 induces CD95L-independent activation-induced cell death in T and B lymphocytes. Brenner D, et al. Blood, 2007 Dec 1. PMID 17712048.
Systematic identification of SH3 domain-mediated human protein-protein interactions by peptide array target screening. Wu C, et al. Proteomics, 2007 Jun. PMID 17474147.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.





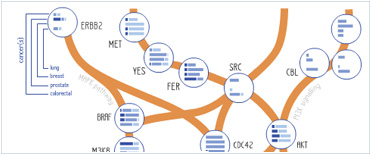







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

